Describe How to Read the Periodic Table Symbols (Atomic Number, Atomic Mass, Period, Family)
The periodic table is the tabular organisation of all the chemical elements on the basis of their corresponding diminutive numbers. In the periodic table, the vertical columns are chosen 'groups' and the horizontal rows are called 'periods'. The modern periodic table is based on the modern periodic law put forward by the English physicist Henry Moseley, which states that "the backdrop of elements are periodic functions of their diminutive numbers". Periodic trends in the backdrop of the elements tin can exist observed downward the groups and across the periods of the modern periodic tabular array.
Table of Content
- Elements on the periodic table
- Related Videos on Periodic Table of Elements
- Listing of Chemic Elements
- Diminutive Number of Elements
- FAQs
Elements on The Periodic Tabular array
Every element has a specific atomic number, which provides insight into the number of protons present within its nucleus. All isotopes of an element fall under a single cell on the periodic table, since they all share the same atomic number.
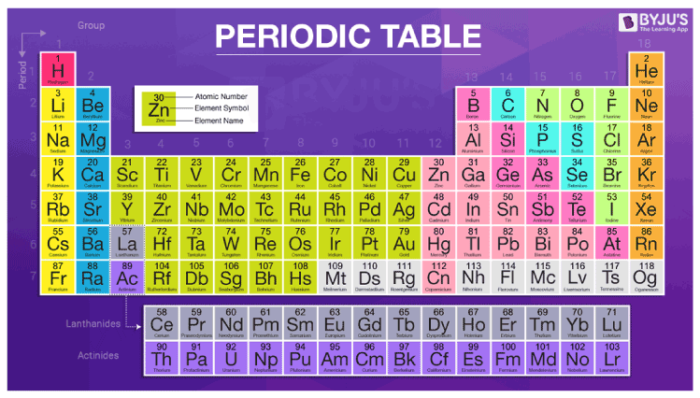
Periodic Tabular array of Elements – Atomic Number, Diminutive Mass, Groups & Symbols
Also, Bank check ⇒
- Periodic Trends in Atomic Radii
- Periodic Trends in Ionic Radii
- Periodic Trends in Electronegativity
- Periodic Trends in Electron Affinity
- Periodic Trends in Ionization Energy
Listing of Chemic Elements
The table below consists of 118 elements of the periodic table, sorted by atomic number, atomic weight, symbols, density, discovered yr and the group.
Diminutive Number of Elements
At that place are about ninety elements found on Earth. Each one has a dissimilar number of protons, electrons and neutrons. The total number these subatomic particles held past the respective elements are responsible for their unique properties (including radioactive decay).
The number of protons in the nucleus is chosen the atomic number. The atomic number of each chemical element is unique. The combined number of protons and neutrons in an atom is chosen the diminutive mass number. While the atomic number always stays the aforementioned some elements accept atoms with dissimilar atomic mass numbers. This is because some elements have a dissimilar number of neutrons in the nucleus. Versions of an element with different atomic mass numbers are called isotopes.
Often Asked Questions – FAQs
What is atomic number?
The atomic number of an element is equal to the total number of protons in the nucleus of the atoms of that chemical element. The atomic number tin provide insight into the electronic configuration of the element. For example, carbon has an electron configuration of [He] 2s2 2p2, since its atomic number is 6.
What is the atomic number and mass number?
The number of protons and the number of neutrons shall determine the mass number of an element. Since the isotopes of an element have slightly unlike mass numbers, it calculates the diminutive mass by obtaining the mean of the mass numbers for its isotopes.
Tin two different elements accept the same atomic number?
Atoms from two different elements may have the same neutron count, simply never the same proton count. The number of protons is unique to the chemical element and it represents the number of atoms.
How practise we summate atomic mass?
Add together the mass of protons and neutrons to compute the atomic mass of a single atom of an element. Example: Find the diminutive mass of a carbon isotope which has seven neutrons. From the periodic tabular array you tin can see that carbon has an atomic number of 6, which is its proton number.
Why is diminutive number of import?
Diminutive number is called the number of protons in an atom. This number is very important, because it is unique to a given element's atoms. An element's atoms all have the same number of protons and each chemical element has a different number of protons in its atoms.
Source: https://byjus.com/chemistry/periodic-table-elements/
Post a Comment for "Describe How to Read the Periodic Table Symbols (Atomic Number, Atomic Mass, Period, Family)"